Empowering Lives Through Radiology:
Illuminating Health, Inspiring Hope.
RadNova Club is a volunteer-driven, non-profit organization headquartered in India, committed to enhancing the health and well-being of communities in underdeveloped areas. Our mission focuses on providing essential diagnostic imaging support, comprehensive services, and
specialized training to uplift and transform lives.
Collaborative Synergy
At RadNova Club, we cherish and uphold the value of every member, fostering an environment where diversity is embraced, and every voice is heard. Our organization is built on the foundation of inclusivity and mutual respect, guiding members to act professionally while interacting with both colleagues and patients. We stand committed to championing those in need of a voice, ensuring no discrimination based on race, color, nationality, geography, language, religion, marital or parental status, age, citizenship, sex, sexual orientation, gender identity or expression, or disability.
We believe in the power of free speech, open discourse, and constructive debate within our meetings and across our social media platforms. However, it is our pledge to always engage with every individual with the utmost dignity, kindness, and respect. This approach solidifies our core dedication to delivering outstanding and compassionate care to everyone.
Combating Breast Cancer
- Elevating consciousness about cancer by highlighting its risk elements, prevention strategies, promoting routine screenings, exploring treatment pathways, and supporting survival.
- Facilitating the early identification of cancer via establishing detection centers and initiating mobile screening camps throughout India, with a focus on aiding those less fortunate.
- Offering sustained assistance to economically disadvantaged cancer patients during their treatment journey and beyond through provisions for lodging, rehabilitation, and access to survivor networks.

News Board
Join RadNova Club
RadNova members have a passion for specific causes and we believe in the power of people to make a difference in the community. Team RadNova hold trust, flexibility, and opportunity to work with a varied set of people as key differentiators from other organisations.
We believe in nurturing talent internally and seek new talent to augment our strength. Together, we all grow and build a better world!
You are welcomed If you have energy, drive and a keen interest in serving the community,
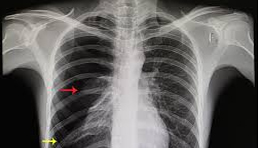
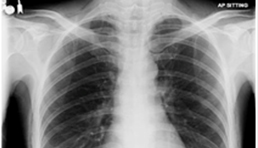
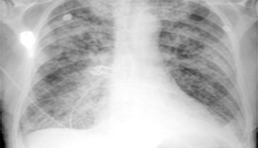
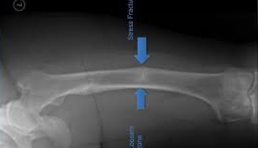
Radiograph
A radiograph, or X-ray, is a medical imaging technique that uses ionizing radiation to visualize internal structures of the body, such as bones and organs, helping diagnose various conditions.
Ultrasonography
Ultrasonography, also known as ultrasound imaging, is a non-invasive diagnostic technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal body structures, including organs, vessels, and tissues.
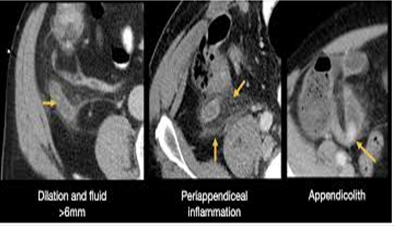
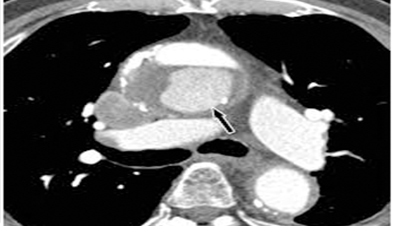
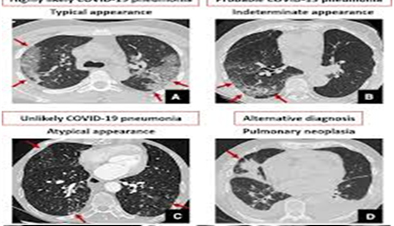
Computed Tomography
Computed Tomography (CT) is a diagnostic tool that combines X-rays and computer technology to produce comprehensive cross-sectional images of the body’s interior, aiding in detecting and assessing a range of medical conditions.
Membership Benefits
4 SIMPLE REASONS
Academic
Regular CME’s and Annual Conferences, Case of the Week and Blogs
Privileges
Contribute to the case of the week, priority/discount in ISHNR events
Nurturing Leadership
Opportunities to be part of various task force, committees of ISHNR
Associations
Connecting with best minds in India and globally in Head and Neck Radiology